Drainage for Paving and Gardens
Every good paving job relies on there being sound drainage, and the same applies to many of our gardens. How do we manage the surface water? What types of pipes are best, or should we use linear channels? How should these be installed? What about land drains? French drains? Soakaways? How can new drainage be connected to the existing, and what about manholes? Find out here.
Drainage for Paving and Gardens
Unless it's permeable paving, a pavement without drainage is doomed to failure. This leading page introduces key concepts and provides definitions of the more commonly used terms. It also provides links to other pages on the site that go into much greater detail regarding key aspects of drainage methods and materials.

Drainage for Pavements
This page explores why drainage is so important to the construction of good quality paving and considers what we do with surface water once it's been collected, and just how much drainage is required on any particular project.

Drainage - A Guide to Installation
Pipework systems comprise modular components, connected to form a system that collects the surface water (or foul), and carries it to another location where it is disposed. This page looks at how those components are fitted together.

Drainage - Foul or Storm? Identifying the System
There are three main forms of drainage system used in Britain and Ireland: Surface or Storm Water; Foul or Grey Water; and Combined, where it's all lumped in together. How do we know which system is which when looking at existing systems?
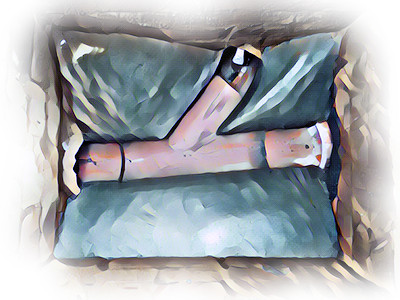
Drainage - Making Connections
How do we go about connecting new drainage via a new access point, such as an access chamber or branch junction? This page looks at the details.

Drainage - Gullies, Gratings and Grids
This page deals with the surface fittings commonly used to drain paved surfaces. The main type of fitting used for this purpose is known as a gully, although it is often incorrectly referred to as a 'grid' amongst the general public.

Drainage - Manholes and Inspection Chambers
This page examines how drainage fixtures and fittings are connected to an existing system via manholes and/or inspection chambers.

Inserting an Inspection Chamber
This page photo-documents the installation of a 450mm diameter pre-fabricated Inspection Chamber (IC) into an existing drainage line in order to facilitate the connection of additional drainage elsewhere on the property.

Drainage - Testing
Installing new drainage is only part of the job. It needs to be tested, to make sure it's both functional and water-tight, so that no water or effluent could escape. Testing can also reveal problems with existing drainage system. This page looks at the tools and techniques that are used.

Drainage - Land Drainage for Fields and Gardens
Land Drainage is, unsurprisingly, the draining of land: the removal of surplus water from the ground, and, in some instances, the returning of cleaned or collected surface water to the ground. This page looks at why it is used, and how it is constructed.

Installing a land drain
This page documents the installation of an interceptor land drain. An interceptor drain is intended to collect groundwater and divert it elsewhere away from a vulnerable area, which might be a pavement, a garden or even a building.

Land Drainage - Fin Drains and Composites
Fin Drains are a modern version of a land drain. They rely on contemporary materials to improve the efficiency and reliability of traditional land drains, whether they are being used to collect water or to redistribute it to the land.
Wet wells, sumps and pumps
Occasionally, there is a need to send water or effluent up a gradient, against gravity. To achieve this, we rely on features such as Wet Wells and so-called Sump-and-Pump arrangements, which are considered on this page.
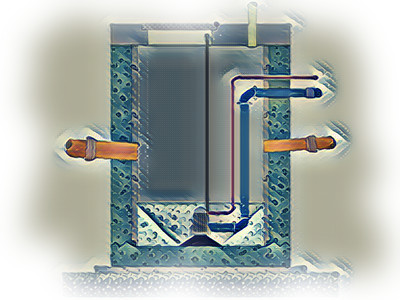
Drainage - Soakaways
Soakaways are a key method of returning collected surface water, or cleaned grey water, to the land. With the increasing usage of SuDS for drainage, the role of soakaways has never been more important, so their construction and they way in which they work needs to be better understood, which is the aim of this page.

Drainage - SUDS
This page aims to provide a basic introduction to the principles of SUDS, Sustainable Drainage Schemes, and its potential for all modern drainage installations.

SUDS - Installing an attenuation cell
A case study detailing the installation of a small attenuation cell (storm crate) soakaway at a residential property.
SUDS - Drive and Patio Infiltration Drain
This page introduces a simple SUDS compliant drainage solution that could be used with most residential driveways, paths and patios.

Threshold Drainage Solutions
Threshold drainage refers to a drainage system installed at the boundary of a pavement where it meets some other surface, such as a public highway or a doorway to a property. This page looks at the special fittings used in such situations.

Linear Channel Drains
Linear Channel Drainage is one of the most popular options for use with paving projects. It offers a cheap, elegant and simple solution that can minimise costly underground pipework installation whilst ensuring surface water is safely removed from a paved area. This page looks at all aspects of linear channels.

Aco Drive Drain - Case Study I
This page is the first of three in a case study which follows the installation of a linear channel drain to a garage threshold as part of a typical block paved driveway construction project. This page looks at the channel system that will be used, and the essential preparatory work.

Aco Drive Drain - Case Study II
This is the second page of a three page case study following the installation of an Aco Drive Drain to a residential driveway. This page looks at the actual installation of the channel and a corner unit.

Aco Drive Drain - Case Study III
This is the final page of three page case study following the installation of an Aco Drive Drain to a residential driveway. This page looks at the at the finishing touches, such as fitting the end caps and gratings.

